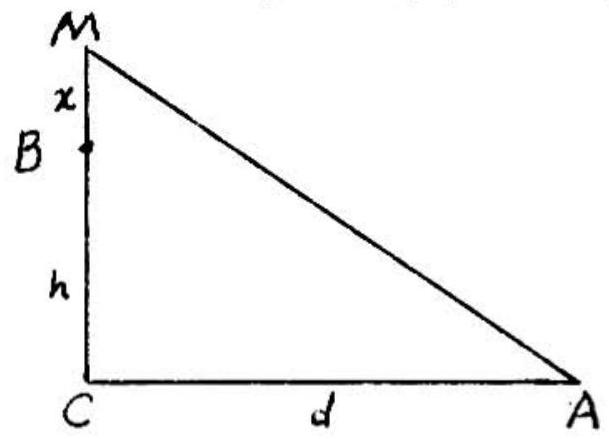
Problem: In the right triangle shown the sum of the distances and is equal to the sum of the distances and . If , and , then equals:
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
.
Problem: In the right triangle shown the sum of the distances and is equal to the sum of the distances and . If , and , then equals:

Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
.