Problem: In triangle ABC,∠C=θ and ∠B=2θ, where 0∘<θ<60∘. The circle with center A and radius AB intersects AC at D and intersects BC, extended if necessary, at B and at E(E may coincide with B). Then EC=AD
Answer Choices:
A. for no values of θ
B. only if θ=45∘
C. only if 0∘<θ≤45∘
D. only if 45∘≤θ<60∘
E. for all θ such that 0∘<θ<60∘
Solution:
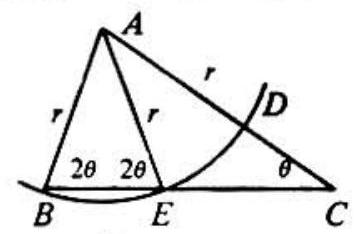
If 0∘<θ<45∘, then (see Figure 1 ) an application of a theorem on exterior angles of triangles to △EAC yields 2θ=∠EAC+θ. Therefore
xEAC=θ and △EAC is isosceles.
Hence EC=AE=AD.
If θ=45∘, then △ABC is a 45∘− 45∘−90∘ triangle and E=B. Then EC=BC=AB=AD.
If 45∘<θ<60∘, then (see Figure 2)
∠EAC=∠EAB+×BAC=[180∘−2(180∘−2θ)]+[180∘−3θ]=θ.
Thus △EAC is isosceles and EC= EA=AD.
.jpg)