¶ 1974 AHSME Problems and Solutions
Individual Problems and Solutions
For problems and detailed solutions to each of the 1974 AHSME problems, please refer below:
Problem 1: If or 4 and or 6 , then is equivalent to
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 2: Let and be such that and . Then equals
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 3: The coefficient of in the polynomial expansion of is
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 4: What is the remainder when is divided by ?
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 5: Given a quadrilateral inscribed in a circle with side extended beyond to point , if and , find
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 6: For positive real numbers and define ; then
Answer Choices:
A. is commutative but not associative
B. is associative but not commutative
C. is neither commutative nor associative
D. is commutative and associative
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 7: A town's population increased by 1,200 people, and then this new population decreased by . The town now had 32 less people than it did before the 1,200 increase. What is the original population?
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 8: What is the smallest prime number dividing the sum ?
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 9: The integers greater than one are arranged in five columns as follows:
(Four consecutive integers appear in each row; in the first, third and other odd numbered rows, the integers appear in the last four columns and increase from left to right; in the second, fourth and other even numbered rows, the integers appear in the first four columns and increase from right to left.)
In which column will the number 1,000 fall?
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 10: What is the smallest integral value of such that has no real roots?
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 11: If and are two points on the line whose equation is , then the distance between and , in terms of and , is
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 12: If and when , then equals
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 13: Which of the following is equivalent to "If is true then is false."?
Answer Choices:
A. P is true or Q is false.
B. If is false then is true.
C. If is false then is true.
D. If Q is true then P is false.
E. If Q is true then P is true.
Solution:
Problem 14: Which statement is correct?
Answer Choices:
A. If , then .
B. If , then .
C. If , then .
D. If , then .
E. If , then .
Solution:
Problem 15: If then equals
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 16: A circle of radius is inscribed in a right isosceles triangle, and a circle of radius is circumscribed about the triangle. Then equals
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 17: If , then equals
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 18: If and , then, in terms of and equals
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 19: In the adjoining figure ABCD is a square and is an equilateral triangle. If the area of is one square inch, then the area of CMN in square inches is
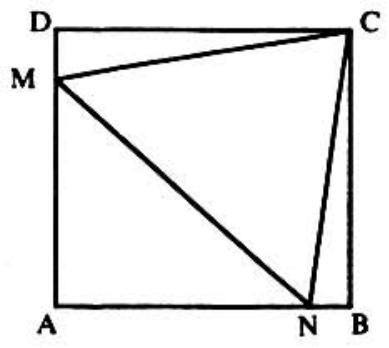
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 20: Let ; then
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 21: In a geometric series of positive terms the difference between the fifth and fourth terms is 576, and the difference between the second and first terms is 9. What is the sum of the first five terms of this series?
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 22: The minimum value of is attained when is
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 23: In the adjoining figure and are parallel tangents to a circle of radius , with and the points of tangency. is a third tangent with as point of tangency. If and then is
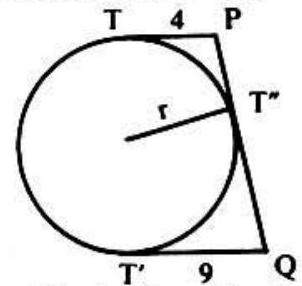
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D. a number other than
E. not determinable from the given information
Solution:
Problem 24: A fair die is rolled six times. The probability of rolling at least a five at least five times is
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 25: In parallelogram of the accompanying diagram, line is drawn bisecting at and meeting (extended) at . From vertex , line is drawn bisecting side at and meeting (extended) at . Lines and meet at . If the area of parallelogram is , then the area of triangle QPO is equal to
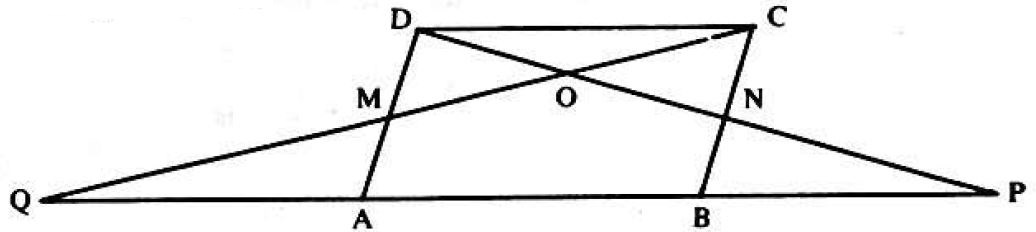
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 26: The number of distinct positive integral divisors of excluding 1 and is
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. none of these
Solution:
Problem 27: If for all real , then the statement: " whenever and and " is true when
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E. The statement is never true
Solution:
Problem 28: Which of the following is satisfied by all numbers of the form
where is 0 or is 0 or is or ?
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D. or
E.
Solution:
Problem 29: For let be the sum of the first 40 terms of the arithmetic progression whose first term is and whose common difference is ; then is
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
Problem 30: A line segment is divided so that the lesser part is to the greater part as the greater part is to the whole. If is the ratio of the lesser part to the greater part, then the value of
is
Answer Choices:
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
Solution:
The problems on this page are the property of the MAA's American Mathematics Competitions