¶ 2026 AIME I Problems and Solutions
Problem 1: Patrick started walking at a constant speed along a straight road from his school to the park. One hour after Patrick left, Tanya started running at a constant speed of miles per hour faster than Patrick walked, following the same straight road from the school to the park. One hour after Tanya left, José started bicycling at a constant speed of miles per hour faster than Tanya ran, following the same straight road from the school to the park. All three people arrived at the park at the same time. The distance from the school to the park is miles, where and are relatively prime positive integers. Find .
Solution:
Problem 2: Find the number of positive integer palindromes written in base , with no zero digits, and whose digits add up to . For example, has these properties. Recall that a palindrome is a number whose representation reads the same from left to right as from right to left.
Solution:
Problem 3: A hemisphere with radius sits on top of a horizontal circular disk with radius , and the hemisphere and disk have the same center. Let be the region of points in the disk such that a sphere of radius can be placed on top of the disk at and lie completely inside the hemisphere. The area of divided by the area of the disk is , where and are relatively prime positive integers. Find .
Solution:
Problem 4: Find the number of integers less than or equal to that are equal to for some choice of distinct positive integers and .
Solution:
Problem 5: A plane contains points and with . Point is rotated in the plane counterclockwise through an acute angle around point to point . Then is rotated in the plane clockwise through angle around point to point . Suppose . The value of can be written as , where and are relatively prime positive integers. Find .
Solution:
Problem 6: The product of all positive real numbers satisfying the equation
is an integer . Find the number of positive integer divisors of .
Solution:
Problem 7: Find the number of functions mapping the set onto such that for every ,
Solution:
Problem 8: Let be the number of positive integer divisors of that leave a remainder of upon division by . Find the remainder when is divided by .
Solution:
Problem 9: Joanne has a blank fair six-sided die and six stickers each displaying a different integer from to . Joanne rolls the die and then places the sticker labeled on the top face of the die. She then rolls the die again, places the sticker labeled on the top face, and continues this process to place the rest of the stickers in order. If the die ever lands with a sticker already on its top face, the new sticker is placed to cover the old sticker. Let be the conditional probability that at the end of the process exactly one face has been left blank, given that all the even-numbered stickers are visible on faces of the die. Then can be written as , where and are relatively prime positive integers. Find .
Solution:
Problem 10: Let have side lengths , , and . Triangle is obtained by rotating about its circumcenter so that is perpendicular to , with and not on the same side of line . Find the integer closest to the area of hexagon .
Solution:
Problem 11: The integers from to are placed in some order into an grid of cells with one number in each cell. Let be the number placed in the cell in row and column , and let be the sum of the absolute differences between adjacent cells. That is,
Find the remainder when the maximum possible value of is divided by .
Solution:
Problem 12: Triangle lies in plane with , , and . Let be the reflection across of the centroid of . Four spheres, all on the same side of , have radii , , , and and are tangent to at points , , , and , respectively. The four spheres are also each tangent to a second plane and are all on the same side of . The value of can be written as , where and are relatively prime positive integers. Find .
Solution:
Problem 13: For each nonnegative integer less than , define
where is defined to be when . That is, is the sum of all binomial coefficients of the form for which and is a multiple of . Find the number of integers in the list that are multiples of the prime number .
Solution:
Problem 14: In an equiangular pentagon, the sum of the squares of the side lengths equals , and the sum of the squares of the diagonal lengths equals . The square of the perimeter of the pentagon can be expressed as , where and are positive integers and is not divisible by the square of any prime. Find .
Solution:
Problem 15: Let , , and be positive integers with both and greater than or equal to and less than or equal to . Define an cell loop in a grid of cells to be the cells that surround an (possibly empty) rectangle of cells in the grid. For example, the following diagram shows a way to partition a grid of cells into cell loops.
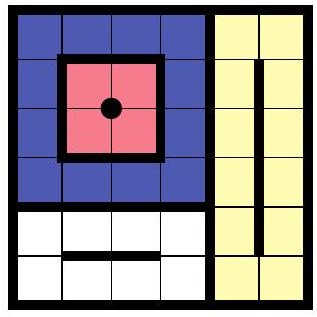
Find the number of ways to partition a grid of cells into cell loops so that every cell of the grid belongs to exactly one cell loop.
Solution:
The problems on this page are the property of the MAA's American Mathematics Competitions